- +91 8329568782
- aglearningsolutions95@gmail.com
SAP S/4 HANA FICO
SAP HANA Career Opportunities – Boost Your Career Growth with SAP HANA
SAP S/4 HANA FICO Training Course In Pune
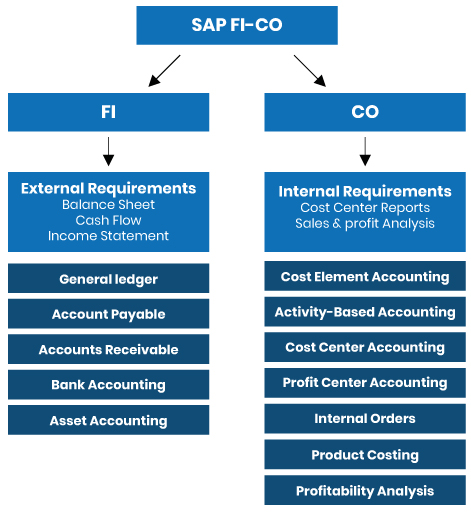
Overview of the SAP FI-CO Module
The FI and CO modules work in tandem to provide a complete picture of the company’s financial situation and internal performance.
- External requirements: The FI module ensures compliance with accounting standards and legal obligations. It ensures financial reports’ accuracy, reliability, and compliance, which are essential for investors, tax authorities, and auditors.
- Internal requirements: The CO module focuses on cost control and strategic decision-making. It enables managers to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and base their decisions on accurate data.
SAP S/4 HANA FICO Training Course In Pune

Overview of the SAP FI-CO Module
The FI and CO modules work in tandem to provide a complete picture of the company’s financial situation and internal performance.
- External requirements: The FI module ensures compliance with accounting standards and legal obligations. It ensures financial reports’ accuracy, reliability, and compliance, which are essential for investors, tax authorities, and auditors.
- Internal requirements: The CO module focuses on cost control and strategic decision-making. It enables managers to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and base their decisions on accurate data.
Focus on the FI Module
SAP’s FI (Financial Accounting) module is designed for accountants and financiers, facilitating the management of financial transactions and the production of reports in line with international and local standards. Its main tools include:
- Balance sheet: Generates financial statements detailing the company’s financial situation at a given point in time, including assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
- Cash flow: Tracking cash flows to assess the company’s ability to generate liquidity.
- Income statement: Details revenues and expenses over a given period, making it possible to assess financial performance.


Focus on the CO Module
SAP’s CO (Controlling) module focuses on controlling and internal cost analysis. It enables strategic decision-making based on accurate data. Its main tools include:
- Reports by cost center: Track and analyze costs to optimize spending.
- Sales and profit analysis: Understanding performance by product and service.
Focus on the CO Module
SAP’s CO (Controlling) module focuses on controlling and internal cost analysis. It enables strategic decision-making based on accurate data. Its main tools include:
- Reports by cost center: Track and analyze costs to optimize spending.
- Sales and profit analysis: Understanding performance by product and service.

Financial Accounting (FI)
SAP S/4HANA Financial Accounting (FI) module is a central component of the SAP S/4HANA ERP suite, designed to support and automate financial processes and ensure regulatory compliance. It offers real-time data processing and analytics capabilities, making it a critical tool for businesses seeking transparent, accurate, and efficient financial management. The S/4HANA version of FI is enhanced with a simplified data model, streamlined processes, and deep integration with other S/4HANA modules and the Universal Journal (ACDOCA), delivering a modern, intelligent finance solution
General Accounting
SAP S/4HANA General Ledger Accounting (FI-GL) is a central component of the Financial Accounting (FI) module that helps organizations manage and record all financial transactions comprehensively. It provides a complete picture of a company’s financial health by integrating data from various processes, such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, asset accounting, and more. SAP S/4HANA’s version of General Ledger Accounting comes with enhancements that leverage the capabilities of the SAP HANA in-memory database, enabling real-time data access, faster processing, and simplified financial operations.
Key Features
Chart of Accounts Management: The General Ledger houses the chart of accounts, which includes the structure and definition of each general ledger account used for financial postings.
Document Posting and Management: This function allows for posting various accounting entries such as journal entries, accruals, deferrals, and more. Each transaction is logged as a document that forms part of the ledger.
Real-time Integration: FI-GL integrates in real-time with other modules like Accounts Receivable (FI-AR), Accounts Payable (FI-AP), Asset Accounting (FI-AA), and more, ensuring that every business transaction immediately reflects in financial statements.
Financial Reporting: General Ledger Accounting provides robust tools for financial reporting, including balance sheets, profit & loss statements, cash flow statements, and more. This enables the preparation of statutory reports and aids decision-making.
Parallel Accounting: This feature supports multiple ledgers, making it easier to meet legal and management accounting requirements. Parallel accounting also allows companies to report in different currencies or according to different accounting standards (e.g., IFRS, GAAP).
Period Closing Activities: FI-GL facilitates month-end and year-end closing processes, including reconciling accounts, making adjustments, and generating financial reports for accurate business performance evaluation.
Accounts receivable (FI-AR)
The Accounts Receivable (AR) sub-module in SAP is a key component of SAP Financial Accounting (FI) and plays a crucial role in managing a company’s customer accounts and transactions. Here are some of its primary features and functions:
1. Customer Master Data Management: This function stores all necessary customer data, such as contact details, credit limits, terms of payment, and more.
2. Customer Invoicing: AR handles the generation, posting, and management of customer invoices. This process often integrates with Sales and Distribution (SD) to streamline billing.
3. Incoming Payments: This module processes and tracks customer payments, matches them against invoices, and handles partial payments and prepayments.
4. Dunning and Credit Management: The AR module helps manage overdue accounts through automated dunning processes and supports credit management for controlling credit limits.
5. Reporting and Analysis: AR provides reports such as customer account balances, aging reports, payment history, and open receivables, helping businesses manage cash flow efficiently.

Key Features
Chart of Accounts Management: The General Ledger houses the chart of accounts, which includes the structure and definition of each general ledger account used for financial postings.
Document Posting and Management: This function allows for posting various accounting entries such as journal entries, accruals, deferrals, and more. Each transaction is logged as a document that forms part of the ledger.
Real-time Integration: FI-GL integrates in real-time with other modules like Accounts Receivable (FI-AR), Accounts Payable (FI-AP), Asset Accounting (FI-AA), and more, ensuring that every business transaction immediately reflects in financial statements.
Financial Reporting: General Ledger Accounting provides robust tools for financial reporting, including balance sheets, profit & loss statements, cash flow statements, and more. This enables the preparation of statutory reports and aids decision-making.
Parallel Accounting: This feature supports multiple ledgers, making it easier to meet legal and management accounting requirements. Parallel accounting also allows companies to report in different currencies or according to different accounting standards (e.g., IFRS, GAAP).
Period Closing Activities: FI-GL facilitates month-end and year-end closing processes, including reconciling accounts, making adjustments, and generating financial reports for accurate business performance evaluation.
Accounts receivable (FI-AR)
The Accounts Receivable (AR) sub-module in SAP is a key component of SAP Financial Accounting (FI) and plays a crucial role in managing a company’s customer accounts and transactions. Here are some of its primary features and functions:
1. Customer Master Data Management: This function stores all necessary customer data, such as contact details, credit limits, terms of payment, and more.
2. Customer Invoicing: AR handles the generation, posting, and management of customer invoices. This process often integrates with Sales and Distribution (SD) to streamline billing.
3. Incoming Payments: This module processes and tracks customer payments, matches them against invoices, and handles partial payments and prepayments.
4. Dunning and Credit Management: The AR module helps manage overdue accounts through automated dunning processes and supports credit management for controlling credit limits.
5. Reporting and Analysis: AR provides reports such as customer account balances, aging reports, payment history, and open receivables, helping businesses manage cash flow efficiently.

Key Features
Vendor Master Data Management: The AP sub-module maintains a central repository of all relevant vendor information, including contact details, payment terms, tax data, and bank account details. Accurate vendor data ensures efficient processing and payment.
Invoice Management: Invoice Verification: AP handles vendor invoices by matching them against purchase orders and goods receipts (three-way match) or by posting direct invoices. This helps ensure accuracy and consistency in vendor payments. Credit Memos: Allows for the creation and processing of credit memos received from vendors, ensuring that credits are appropriately applied to outstanding invoices.
Payment Processing: Automatic Payments Program (APP): This program allows for the automatic scheduling and processing of payments to vendors based on predefined parameters, such as due dates, discount terms, and payment methods.Manual Payments: Provides flexibility to manually process payments when necessary.
Integration with Bank Accounts: FI-AP is integrated with SAP Bank Accounting, facilitating electronic bank statements, payment reconciliation, and processing bank transfers.
Open Item Management: All open vendor invoices are maintained as open items until fully cleared by payments or adjustments. This enables efficient tracking and monitoring of outstanding payables.
Aging and Due Date Analysis: The AP module offers detailed reports for analyzing outstanding payables by age and due dates. This helps businesses manage cash flow by identifying and prioritizing payments.
Tax Management: Accounts Payable supports tax calculations (such as VAT, GST, withholding tax, etc.) in compliance with relevant legal and business requirements during invoice posting.

Integration: The AR sub-module integrates with other SAP modules such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Controlling (CO), and Material Management (MM) for a seamless business process flow, enhancing data consistency and operational efficiency.
Accounts Payable (FI- AP)
The Accounts Payable (FI-AP) component in SAP S/4HANA is an integral part of the Financial Accounting (FI) module that focuses on managing a company’s obligations to pay its creditors. It is designed to optimize and automate the management of vendor-related financial processes, including invoice processing, payment handling, and integration with other components like Materials Management (MM) and Bank Accounting (FI-BL). S/4HANA brings significant enhancements to FI-AP, leveraging real-time data processing, streamlined workflows, and integration with SAP Fiori apps for a better user experience.
Integration With Other Modules
The AP sub-module works in sync with Material Management (MM) for purchase orders and goods receipt/invoice receipt (GR/IR) processes, ensuring the entire procure-to-pay cycle is efficiently managed.
Data automatically flows to the General Ledger (FI-GL), ensuring that all payables transactions are reflected correctly in financial statements.
BHANK ACCOUNTING (FI-BL)
The AP sub-module works in sync with Material Management (MM) for purchase orders and goods receipt/invoice receipt (GR/IR) processes, ensuring the entire procure-to-pay cycle is efficiently managed.
Data automatically flows to the General Ledger (FI-GL), ensuring that all payables transactions are reflected correctly in financial statements.

Key Features FI-BL:
Bank Master Data Management: Bank Master Records store essential information such as bank name, address, bank account numbers, SWIFT/BIC codes, and other relevant details. This data is used for processing transactions with banks and managing electronic communication.
Bank Accounts Management: The sub-module allows for the creation and management of company bank accounts, specifying account types (e.g., current accounts, savings accounts) and account control features. This makes it easier to handle various banking activities systematically.
Automatic and Manual Payment Processing: Automatic Payment Program (APP): This feature enables the automation of vendor and customer payment processes. It handles batch payments based on predefined rules, such as due dates, payment methods, and bank preferences. Manual Payments: SAP Bank Accounting supports manual payments, including issuing checks or performing bank transfers.
Bank Statement Processing and Reconciliation: Electronic Bank Statement (EBS): EBS allows for importing and processing bank statements electronically in SAP, reducing manual workload. EBS matches bank transactions (deposits, withdrawals) with open items in the system, facilitating efficient reconciliation. Manual Bank Reconciliation: Companies can reconcile their bank statements manually by matching external bank transactions with internal records.
Check Management: FI-BL supports check handling processes, such as issuing, voiding, printing, and reconciling checks. It helps manage all stages of check lifecycle, ensuring proper control and visibility
Cash Management Integration: The sub-module integrates with Cash Management to provide visibility into the organization’s cash flow, offering tools to forecast and control cash movements across bank accounts.
Lockbox Processing (for the US): This feature is especially useful for companies in the United States, enabling automated and efficient processing of incoming payments made via lockbox services offered by banks.
Bank Communication Management: FI-BL facilitates secure communication between SAP and banks, supporting formats like SWIFT MT940 for international banking transactions and other country-specific protocols.
Liquidity Management: The Bank Accounting module works with the Liquidity Planning tools to forecast and analyze cash flows, improving overall liquidity management.
Asset Accounting(FI-AA)
The Asset Accounting (FI-AA) sub-module in SAP S/4HANA has undergone significant enhancements compared to the traditional SAP ERP system, making it more efficient and capable of meeting modern accounting needs. It is designed to help organizations track, manage, and control their fixed assets seamlessly across their lifecycle within the SAP S/4HANA Finance environment. The module integrates deeply with the Universal Journal (table ACDOCA), which consolidates all financial and controlling data, improving data transparency and processing speed.

Key Features and Enhancements of SAP S/4HANA Asset Accounting:
Universal Journal Integration:
All asset transactions, such as acquisitions, transfers, retirements, and depreciation, are posted directly to the Universal Journal (ACDOCA) table. This unified approach ensures consistency and eliminates data redundancies, simplifying financial closing processes.
Real-Time Data: Asset transactions reflect instantly in financial reports, providing real-time insights into asset values, depreciation, and financial status.
Parallel Valuation and Ledger Handling:
Unlike traditional systems, SAP S/4HANA Asset Accounting supports multiple valuation views (e.g., IFRS, local GAAP, or tax valuation) in a single accounting principle using parallel ledgers. This allows for flexible and comprehensive reporting based on different accounting standards.
Simplified handling of parallel accounting eliminates the need for complex reconciliation tasks, as all valuations are managed consistently and transparently.
Simplified Data Structures:
The data model for Asset Accounting has been simplified, reducing the number of tables involved. As a result, reporting and data retrieval are faster, and system performance is improved.
Depreciation Calculation and Posting:
Depreciation runs in SAP S/4HANA are faster and leverage parallel processing capabilities.
Real-time integration ensures that depreciation is always up-to-date, with postings directly visible in the Universal Journal.
Integrated Asset Transactions:
The sub-module integrates seamlessly with General Ledger (FI-GL), Accounts Payable (FI-AP), Controlling (CO), and Materials Management (MM) modules. This integration ensures accurate and complete asset transaction processing, including purchases, transfers, and retirements.
Asset Master Data Enhancements:
Asset master data management has been streamlined with improved interfaces, making it easier to create and update asset records. The system also supports asset hierarchies and component structures to better represent complex assets.
Multiple Depreciation Areas:
SAP S/4HANA allows managing multiple depreciation areas for different valuation views. Depreciation values can be posted either in real-time or periodically, depending on business needs.
Automatic Adjustments and Revaluations:
Asset values can be adjusted or revalued automatically based on changes in business or tax requirements. The flexibility to handle revaluations or impairments ensures compliance with different accounting standards.
Enhanced Reporting Capabilities:
With the SAP S/4HANA system, advanced reporting tools, including SAP Fiori apps, provide intuitive and real-time insights into asset data. Key reports like Asset History Sheet, Depreciation Overview, and other analytical dashboards are easily accessible and highly customizable.
Asset Lifecycle Management:
FI-AA in S/4HANA covers the complete asset lifecycle, from acquisition and capitalization through operational phases to retirement or scrapping. The lifecycle view offers better management, tracking, and decision-making capabilities.
Integration with Financial Closing Cockpit:
Asset Accounting integrates into the SAP S/4HANA Financial Closing Cockpit, helping organizations streamline their period-end and year-end closing activities for asset transactions.
SAP S/4HANA Controlling (CO)
SAP S/4HANA Controlling (CO) is a key module within the SAP S/4HANA ERP system, designed to support the internal management and decision-making processes of an organization. It provides tools for planning, reporting, and monitoring costs and revenues, enabling businesses to perform effective cost controlling, profitability analysis, and internal management accounting. S/4HANA CO is tightly integrated with other modules, such as Financial Accounting (FI), Production Planning (PP), Sales and Distribution (SD), and Materials Management (MM), ensuring comprehensive financial and operational data consistency.

Key Features and Components of SAP S/4HANA Controlling (CO):
Cost Element Accounting (CO-OM-CEL):
Cost elements classify costs based on their origin, enabling detailed cost tracking and assignment.Primary cost elements represent costs originating from external sources (linked to G/L accounts in FI), while secondary cost elements represent internal cost flows.
Parallel Valuation and Ledger Handling:
Allows businesses to assign costs to cost centers, reflecting organizational structure (e.g., departments, functions).Enables tracking of fixed and variable costs for cost centers, helping monitor performance against budgets.
Internal Orders (CO-OM-OPA):
Internal orders are used to track costs and revenues for temporary, specific tasks, or projects (e.g., marketing campaigns, R&D activities).Costs can be tracked and settled to cost centers, profitability segments, projects, or fixed assets, providing detailed visibility and control
Profitability Analysis (CO-PA):
Provides insights into the profitability of various market segments such as products, customers, or sales regions.Two forms of CO-PA are available:
Account-Based CO-PA (integrated with the Universal Journal for real-time data).
Costing-Based CO-PA (traditional, offers more detailed cost allocations).
Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC):
Product Cost Planning (PCP), Cost Object Controlling (COC), and Actual Costing / Material Ledger (ML).
Product Cost Planning (PCP): Provides tools for cost estimates of manufactured products, including standard costs.
Cost Object Controlling (COC): Tracks costs for production orders, process orders, sales orders, and projects, allowing businesses to analyze actual vs. planned costs.
Material Ledger (ML): In S/4HANA, the Material Ledger is mandatory and offers detailed tracking of material movements and actual costs, providing insights into variances and inventory values.
Profit Center Accounting (EC-PCA):
Allows companies to assess the profitability of different segments within the business (e.g., product lines, regions).
Profit centers can be used to simulate company divisions for internal reporting, enabling effective performance evaluation.
Activity-Based Costing (ABC):
Distributes overhead costs to cost objects based on activities, providing a more accurate view of costs associated with processes, products, or services.Helps in identifying cost drivers and optimizing resource allocation.
Integrated Planning and Budgeting:
The CO module supports planning and budgeting processes for cost centers, profit centers, and internal orders.Integration with SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) enables advanced planning scenarios and predictive analytics.
Cost Allocation and Settlement:
Flexible cost allocation methods (distribution, assessments, and overhead rates) enable accurate cost allocation to various cost objects.Settlement processes ensure costs are assigned to the correct objects (e.g., cost centers, WBS elements, assets) for accurate reporting.
Real-Time Integration with Financial Accounting (FI):
All postings in CO reflect immediately in FI through integration with the Universal Journal (ACDOCA), ensuring data consistency and transparency across financial and management accounting.Real-time updates eliminate the need for batch reconciliations, reducing closing times.
Simplified Data Model:
S/4HANA CO features a streamlined data model, leveraging the Universal Journal for consolidated data storage, providing a single source of truth for FI and CO data.This reduces redundancies, accelerates reporting, and simplifies processes.
Enhanced User Experience with SAP Fiori:
SAP Fiori apps enable an intuitive, role-based experience for CO users. Apps support tasks such as cost center monitoring, budget planning, and profitability analysis, making navigation simpler and more efficient.